Plessy v ferguson answer key – Step into the annals of history as we delve into Plessy v. Ferguson Answer Key, a pivotal Supreme Court case that shaped the trajectory of race relations in America. This in-depth exploration will illuminate the legal arguments, societal context, and lasting impact of this landmark decision.
The infamous “separate but equal” doctrine, the legal climate of the Jim Crow era, and the enduring legacy of Plessy v. Ferguson will be meticulously examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of this pivotal moment in American jurisprudence.
Plessy v. Ferguson

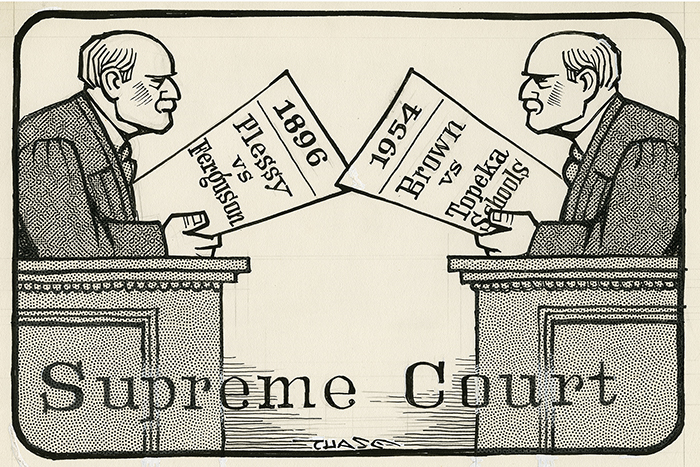
Plessy v. Ferguson was a landmark Supreme Court case that ruled that racial segregation in public facilities was constitutional. The case was decided in 1896, and its ruling was used to justify the implementation of Jim Crow laws throughout the United States.
Historical Context
The Plessy v. Ferguson case was decided during a time of intense racial discrimination in the United States. The post-Reconstruction era was a period of widespread violence and oppression against African Americans, and the Jim Crow laws were a system of legal segregation that enforced white supremacy.
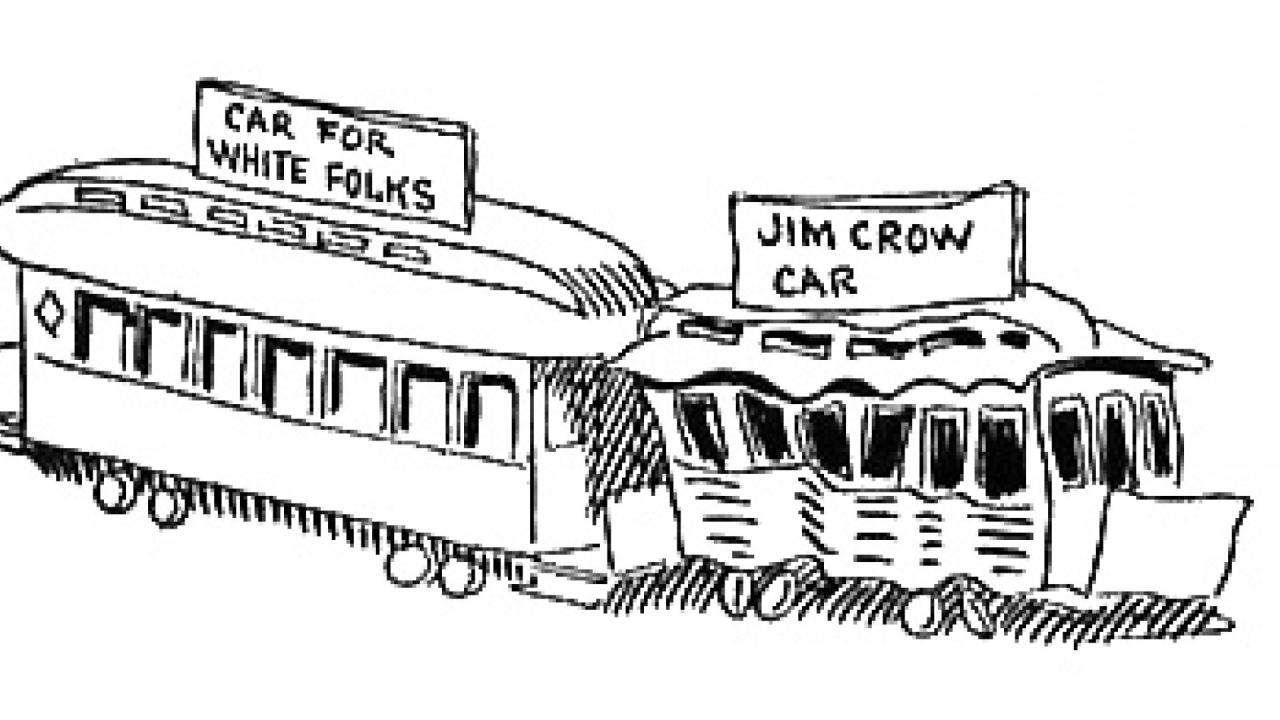
Jim Crow laws varied from state to state, but they all shared the common goal of separating African Americans from whites in every aspect of life. African Americans were forced to attend segregated schools, ride in segregated train cars, and eat in segregated restaurants.
They were also denied the right to vote, serve on juries, or hold public office.
The Jim Crow laws had a devastating impact on the lives of African Americans. They were denied equal access to education, employment, and housing. They were subjected to violence and intimidation, and they were forced to live in a state of constant fear.
The Plessy v. Ferguson case was a major setback for the civil rights movement. The Supreme Court’s ruling upheld the constitutionality of Jim Crow laws, and it gave legal sanction to the system of racial segregation that would last for decades.
Legal Arguments in Plessy v. Ferguson
In Plessy v. Ferguson, both sides presented legal arguments to support their positions. The primary issue in the case was the constitutionality of Louisiana’s Separate Car Act, which required separate railway carriages for white and black passengers.
Arguments for the State of Louisiana, Plessy v ferguson answer key
- The state argued that the Separate Car Act was a legitimate exercise of its police power to promote public safety and order.
- The state also argued that the act did not violate the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment because it provided separate but equal accommodations for black and white passengers.
Arguments for Homer Plessy
- Plessy argued that the Separate Car Act was unconstitutional because it violated the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
- Plessy argued that the act created an arbitrary and unreasonable classification based on race, and that it denied black passengers the equal protection of the laws.
The “Separate but Equal” Doctrine
The Supreme Court’s decision in Plessy v. Ferguson established the “separate but equal” doctrine. This doctrine held that states could provide separate facilities for different races, as long as the facilities were equal in quality.
The “separate but equal” doctrine was used to justify racial segregation in many areas of American life, including schools, transportation, and public accommodations.
Arguments for and Against the Constitutionality of Segregation
There were many arguments for and against the constitutionality of segregation. Supporters of segregation argued that it was necessary to maintain social order and prevent racial conflict.
Opponents of segregation argued that it was a violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. They also argued that segregation perpetuated racial inequality and discrimination.
Supreme Court Decision and Impact

In 1896, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of the state of Louisiana in the case of Plessy v. Ferguson. The Court upheld the constitutionality of the state’s Separate Car Act, which required railroads to provide separate but equal accommodations for white and black passengers.
Reasoning Behind the Court’s Ruling
The Court’s ruling was based on the “separate-but-equal” doctrine. This doctrine held that segregation was constitutional as long as the facilities provided for each race were equal in quality.
Immediate and Long-Term Impact
The decision in Plessy v. Ferguson had a profound impact on American society. It legalized segregation and provided a legal basis for the Jim Crow system of racial discrimination that existed in the South for the next half-century.
While the Plessy v. Ferguson answer key provided insights into the complexities of racial segregation, the climax of O. Henry’s “Gift of the Magi” offers a poignant reminder of the sacrifices we make for those we love. The story’s poignant resolution echoes the enduring impact of Plessy v.
Ferguson, underscoring the importance of empathy and understanding in a society grappling with the legacy of inequality.
The decision also had a long-term impact on the civil rights movement. It took nearly 60 years for the Supreme Court to overturn Plessy v. Ferguson in the landmark case of Brown v. Board of Education (1954).
Legacy of Plessy v. Ferguson
The legacy of Plessy v. Fergusonextends far beyond the specific case and has had a profound impact on American law and society.
Subsequent Supreme Court Decisions
Plessy v. Fergusonestablished the “separate-but-equal” doctrine, which allowed for the segregation of public facilities based on race. This doctrine was upheld in subsequent Supreme Court decisions, including Cumming v. Richmond County Board of Education(1899) and McCabe v. Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railway Co.(1914).
Rise of the Civil Rights Movement
The injustice of the “separate-but-equal” doctrine fueled the rise of the Civil Rights Movement. Activists argued that separate facilities were inherently unequal and violated the Fourteenth Amendment’s guarantee of equal protection under the law.
Overturning of Plessy v. Ferguson
In 1954, the Supreme Court overturned Plessy v. Fergusonin the landmark case Brown v. Board of Education. The Court ruled that “separate educational facilities are inherently unequal” and that racial segregation in public schools violated the Equal Protection Clause.
FAQ Summary: Plessy V Ferguson Answer Key
What was the central legal question in Plessy v. Ferguson?
The case centered on the constitutionality of racial segregation in public facilities, specifically railroad cars.
How did the Supreme Court rule in Plessy v. Ferguson?
The Court upheld the “separate but equal” doctrine, ruling that segregation was constitutional as long as the facilities provided for different races were equal in quality.
What was the long-term impact of Plessy v. Ferguson?
The decision entrenched racial segregation in American society for decades and became a cornerstone of the Jim Crow system. It was eventually overturned by the Supreme Court in Brown v. Board of Education in 1954.

