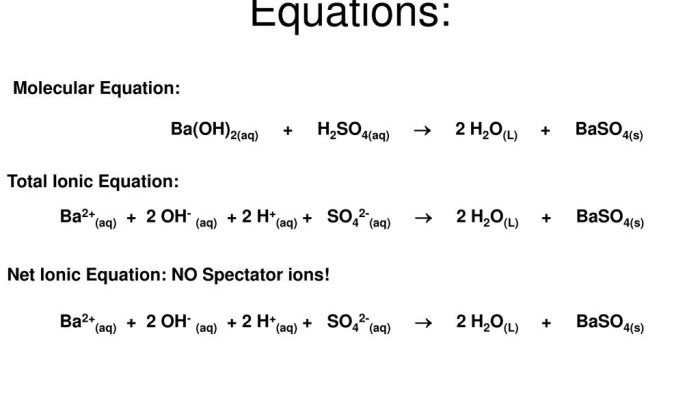
Embark on a captivating journey with the Mystery of Matter Worksheet Answer Key, where the fundamental building blocks of the universe are unveiled. This comprehensive guide unlocks the secrets of matter, revealing its composition, structure, and interactions with energy. Prepare to delve into the fascinating realm of protons, neutrons, and electrons, unraveling the mysteries that govern the physical world.
Our exploration begins with the fundamental particles that constitute matter, delving into their properties and the forces that bind them together. We’ll uncover the intricacies of atomic structure and bonding, examining the role of valence electrons in shaping the chemical behavior of substances.
The journey continues through the states of matter, exploring the factors that determine whether a substance exists as a solid, liquid, or gas.
Matter Composition and Properties: Mystery Of Matter Worksheet Answer Key
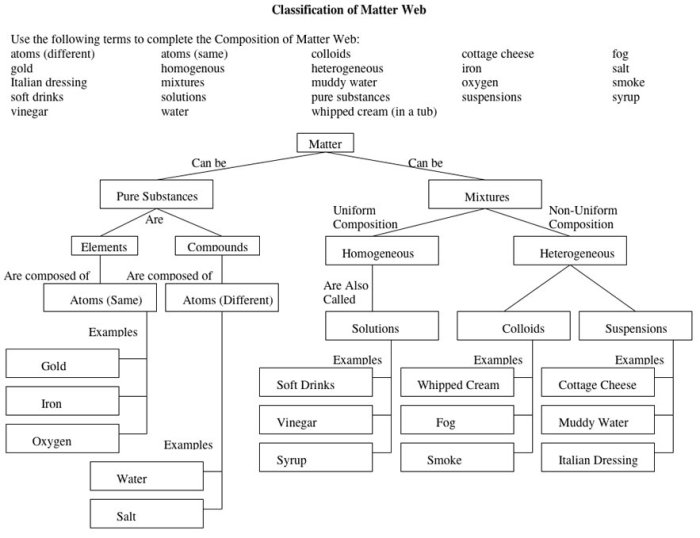
Matter is composed of fundamental particles known as protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the atom’s nucleus, while electrons orbit around it.
| Particle | Charge | Mass (amu) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | 0 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Electron | -1 | 0.0005 | Electron cloud |
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in its nucleus, determining its identity. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons, indicating the mass of an atom.
Atomic Structure and Bonding
An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by an electron cloud.
Chemical bonds form between atoms to create molecules. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons, ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, and metallic bonds involve the sharing of valence electrons.
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom, and they determine the chemical properties of the element.
States of Matter, Mystery of matter worksheet answer key
Matter exists in three primary states: solid, liquid, and gas.
| State | Properties |
|---|---|
| Solid | Fixed shape and volume, rigid |
| Liquid | No fixed shape, takes the shape of its container, flows |
| Gas | No fixed shape or volume, fills its container |
Temperature and pressure influence the state of matter. For example, increasing temperature can change a solid to a liquid or a liquid to a gas.
Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical changes involve changes in the form or appearance of matter, without altering its chemical composition. Examples include melting, freezing, and boiling.
Chemical changes involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. Examples include combustion, rusting, and digestion.
Physical and chemical changes can be used to separate and purify substances.
Energy and Matter Interactions
Energy can interact with matter in various forms, such as heat, light, and electricity.
Energy can be transferred between matter and its surroundings. For example, heat can be transferred from a hot object to a cold object.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed.
General Inquiries
What are the fundamental particles of matter?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
How does atomic number relate to the composition of matter?
Atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom, determining the element’s identity
What factors influence the state of matter?
Temperature and pressure
How can physical and chemical changes be used to separate substances?
Physical changes involve changes in physical properties without altering chemical composition, while chemical changes involve the formation of new substances