Ecology Living Environment Regents Questions delve into the intricate web of life, exploring the dynamic interactions between organisms and their environment. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the subject, equipping readers with a thorough understanding of the fundamental concepts and their real-world applications.
From the intricate workings of ecosystems to the human impact on the environment, this guide unravels the complexities of ecology, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and foster a sustainable future.
Ecosystems and Communities: Ecology Living Environment Regents Questions

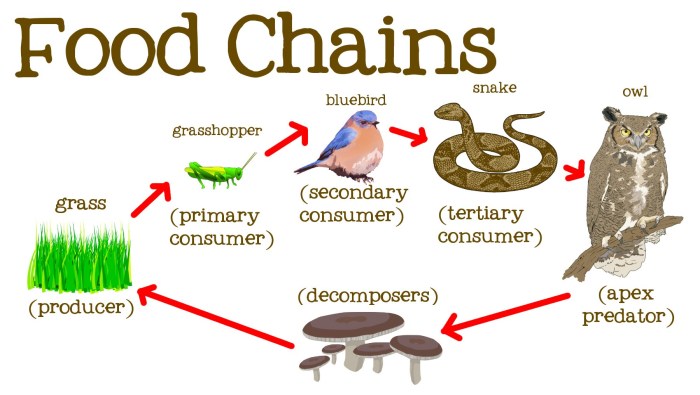
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their physical environment interacting as a system. Components of an ecosystem include producers (autotrophs), consumers (heterotrophs), decomposers, and the non-living environment. Interactions between these components include predator-prey relationships, competition, symbiosis, and nutrient cycling.
Different types of ecosystems exist, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, and aquatic ecosystems. Each ecosystem has unique characteristics, such as climate, vegetation, and animal life.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms within an ecosystem. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem stability by providing resilience against environmental disturbances and supporting a wide range of ecosystem services, such as food production, water purification, and climate regulation.
Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycling

Energy flows through an ecosystem from producers to consumers. Producers, such as plants, use sunlight to convert inorganic matter into organic matter through photosynthesis. Consumers, such as animals, obtain energy by consuming producers or other consumers.
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients are then available for producers to use in photosynthesis, completing the nutrient cycle.
Importance of Energy and Nutrient Flow, Ecology living environment regents questions
Energy and nutrient flow are essential for ecosystem function. Energy provides the power for all life processes, while nutrients are necessary for growth and development. Disruptions in energy or nutrient flow can have significant consequences for ecosystem stability and the survival of organisms within it.
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics refers to the changes in the size and structure of a population over time. Factors influencing population growth and decline include birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
Population Growth Curves
Population growth curves describe the pattern of population change over time. Different types of growth curves exist, such as exponential growth, logistic growth, and stable growth. Each curve has implications for the carrying capacity of the environment and the sustainability of the population.
Carrying Capacity
Carrying capacity is the maximum population size that an environment can support indefinitely without degrading its resources. When a population exceeds its carrying capacity, it can lead to competition, starvation, disease, and other negative consequences.
Human Impact on the Environment
Human activities have a profound impact on the environment. Major activities that contribute to environmental degradation include pollution, habitat loss, and climate change.
Consequences of Human Activities
Pollution, habitat loss, and climate change have severe consequences for ecosystems and human well-being. Pollution can contaminate water, soil, and air, harming organisms and ecosystems. Habitat loss reduces biodiversity and disrupts ecosystem services. Climate change alters weather patterns, sea levels, and ecosystems, leading to widespread impacts on both natural and human systems.
Mitigation Strategies
Mitigating human impact on the environment requires collective action and sustainable practices. Strategies include reducing pollution, protecting habitats, promoting renewable energy, and adapting to climate change.
Environmental Conservation and Management
Environmental conservation and management aim to protect and restore the environment for future generations. Conservation approaches include establishing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, and promoting sustainable practices, such as responsible resource use and waste management.
Importance of Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for preserving biodiversity, maintaining ecosystem services, and ensuring human well-being. Protecting and restoring the environment helps mitigate climate change, safeguard water resources, and provide food security for future generations.
Role of Stakeholders
Government, organizations, and individuals all play a vital role in environmental stewardship. Governments establish policies and regulations to protect the environment, organizations implement conservation programs and promote sustainable practices, and individuals make informed choices that minimize their environmental impact.
FAQs
What are the key components of an ecosystem?
Producers, consumers, decomposers, and non-living factors.
How does energy flow through an ecosystem?
From producers to consumers, with decomposers recycling nutrients back into the system.
What factors influence population growth?
Birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
What is the concept of carrying capacity?
The maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely.