In the realm of accounting, prepare journal entries to record transactions a through h is a fundamental process that underpins the accuracy and reliability of financial records. This guide delves into the intricacies of journal entries, empowering readers with the knowledge and skills to effectively capture and analyze business transactions.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the purpose and function of journal entries, dissect the different types and their uses, and delve into the principles and rules that govern their analysis. We will then provide a step-by-step guide to recording transactions in a journal, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and completeness.
Finally, we will examine the process of posting journal entries to the ledger and analyze their impact on financial statements.
1. Define Journal Entries
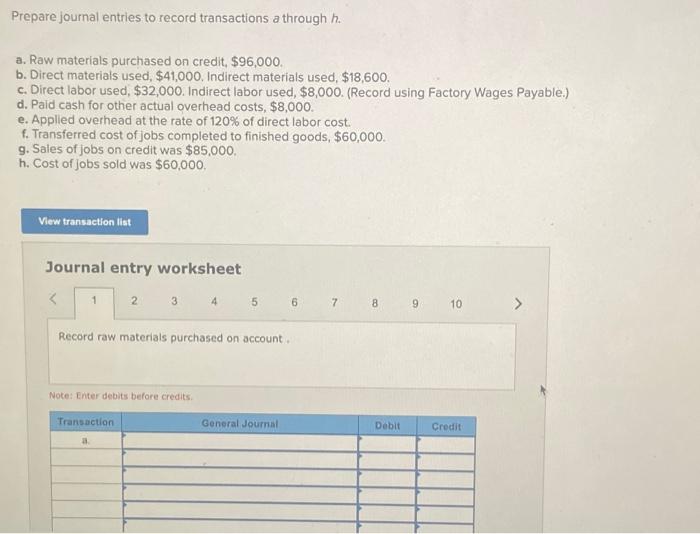
Journal entries are the fundamental building blocks of accounting. They provide a systematic and chronological record of all financial transactions entered into by a business. Each transaction is recorded in a journal entry, which includes the date, a brief description of the transaction, and the accounts affected along with their respective debit and credit amounts.
The primary purpose of journal entries is to provide a detailed and auditable trail of all business transactions. This allows accountants and auditors to trace the flow of funds through the accounting system and to ensure that all transactions have been properly recorded and accounted for.
Types of Journal Entries
- Simple journal entriesrecord a single transaction involving two accounts.
- Compound journal entriesrecord a single transaction involving more than two accounts.
- Adjusting journal entriesare made at the end of an accounting period to correct errors, update account balances, and reflect the accrual and deferral of expenses and revenues.
- Closing journal entriesare made at the end of an accounting period to close temporary accounts and transfer their balances to permanent accounts.
- Reversing journal entriesare made at the beginning of a new accounting period to reverse the effects of adjusting journal entries made at the end of the previous period.
2. Analyze Transactions
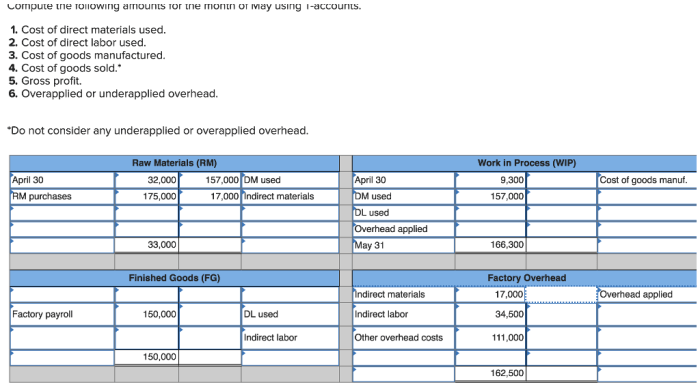
The first step in recording a journal entry is to analyze the transaction and identify the accounts affected. This requires an understanding of the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) and the double-entry bookkeeping system. Once the accounts affected have been identified, the next step is to determine the debit and credit amounts for each account.
Accounting Principles and Rules
- Debit the asset and expense accounts; credit the liability, revenue, and equity accounts.
- The total debits must equal the total credits for each journal entry.
- Transactions must be recorded in the period in which they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
- Transactions must be supported by source documents, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements.
3. Record Transactions
To record a transaction in a journal, the following steps should be followed:
- Enter the date of the transaction.
- Write a brief description of the transaction.
- Identify the accounts affected and enter the debit and credit amounts.
- Total the debit and credit columns to ensure that they are equal.
- Post the journal entry to the ledger.
Importance of Accuracy and Completeness
It is important to record transactions accurately and completely in order to maintain the integrity of the accounting records. Inaccurate or incomplete journal entries can lead to errors in the financial statements and make it difficult to track the flow of funds through the business.
4. Post Journal Entries
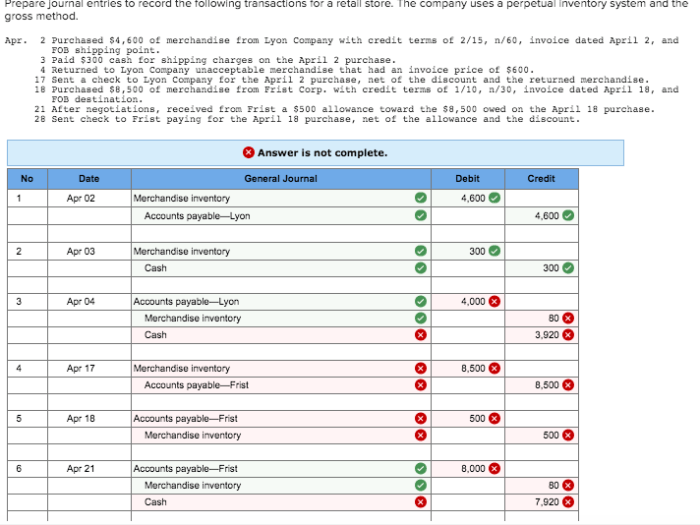
Posting journal entries to the ledger is the process of transferring the debit and credit amounts from the journal to the appropriate ledger accounts. This is done in order to update the account balances and to provide a more detailed record of all transactions.
Methods of Posting Journal Entries, Prepare journal entries to record transactions a through h
- T-accountsare individual accounts that are used to track the debits and credits for each account.
- Ledger cardsare similar to T-accounts, but they are typically used for accounts with a high volume of transactions.
- Computerized accounting systemscan automatically post journal entries to the ledger.
5. Analyze the Impact of Transactions: Prepare Journal Entries To Record Transactions A Through H
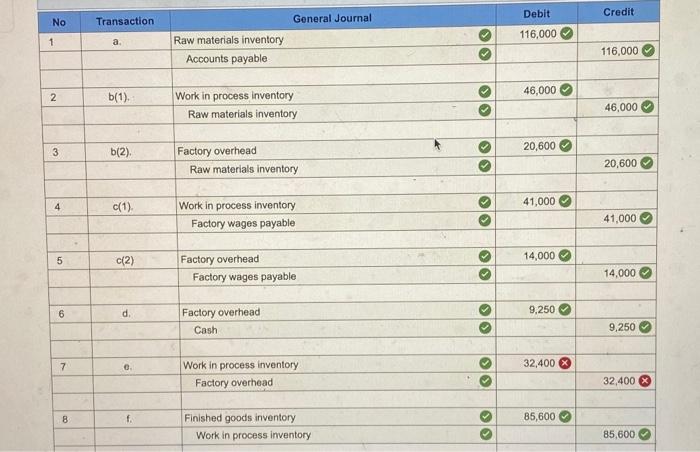
Journal entries can be used to track and analyze business activities. By analyzing the debits and credits in each journal entry, accountants can gain insights into the financial performance of the business.
For example, an increase in sales revenue will result in a debit to the Cash account and a credit to the Sales Revenue account. This information can be used to track sales trends and to make informed decisions about pricing and marketing strategies.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of a journal entry?
A journal entry is a record of a financial transaction that has occurred. It provides a detailed description of the transaction, including the date, the accounts affected, and the debit and credit amounts.
What are the different types of journal entries?
There are many different types of journal entries, including cash receipts, cash disbursements, sales, purchases, and adjustments.
How do I record a transaction in a journal?
To record a transaction in a journal, you need to identify the accounts affected by the transaction and determine the debit and credit amounts for each account.
What is the importance of accuracy and completeness in recording transactions?
Accuracy and completeness are essential in recording transactions because they ensure that the financial records are reliable and can be used to make informed decisions.