Which description of skeletal cartilage is incorrect – Unveiling the inaccuracies surrounding skeletal cartilage, this exploration delves into the realm of its composition, structure, and functions. By examining incorrect descriptions and contrasting them with accurate ones, we embark on a journey to illuminate the true nature of this vital tissue.
Skeletal cartilage, a specialized connective tissue, plays a crucial role in supporting and protecting various structures within our bodies. However, misconceptions and incorrect descriptions can cloud our understanding of its characteristics and significance. This discourse aims to rectify these inaccuracies, providing a comprehensive and authoritative account of skeletal cartilage.
Overview of Skeletal Cartilage
Skeletal cartilage is a specialized connective tissue that provides structural support and flexibility to the body. It is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes, which are embedded in a matrix of collagen and other proteins.
There are three main types of skeletal cartilage:
- Hyaline cartilage: The most common type of skeletal cartilage, found in the articular surfaces of joints, the rib cage, and the nose.
- Elastic cartilage: Found in the ears and epiglottis, it provides flexibility and resilience.
- Fibrocartilage: The strongest type of skeletal cartilage, found in the intervertebral discs and menisci of the knee.
Incorrect Descriptions of Skeletal Cartilage
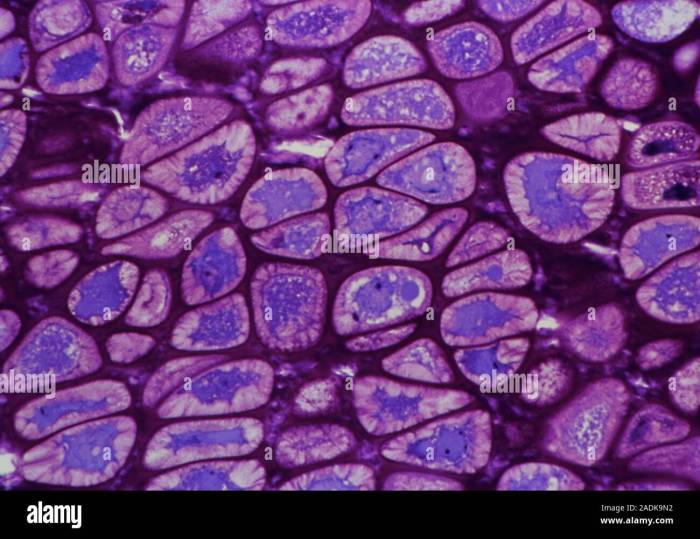
One incorrect description of skeletal cartilage is that it is a type of bone. While skeletal cartilage and bone share some similarities, such as providing structural support, they are distinct tissues with different compositions and properties.
Another incorrect description is that skeletal cartilage is composed of blood vessels. Unlike bone, skeletal cartilage is avascular, meaning it does not contain blood vessels. Nutrients and oxygen are instead diffused through the matrix.
Correct Descriptions of Skeletal Cartilage
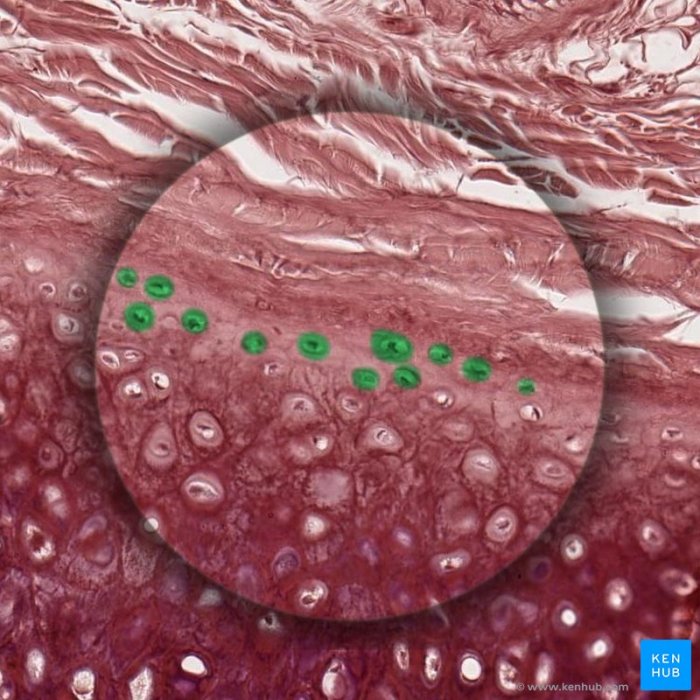
Skeletal cartilage is characterized by its flexibility, resilience, and ability to withstand compressive forces. It is composed of chondrocytes embedded in a matrix of collagen and other proteins.
The following are some of the key characteristics of skeletal cartilage:
- Avascular: Skeletal cartilage does not contain blood vessels.
- Flexible: Skeletal cartilage is more flexible than bone, allowing it to bend and withstand compressive forces.
- Resilient: Skeletal cartilage can withstand repeated bending and compression without breaking.
- Low friction: The smooth surface of skeletal cartilage reduces friction in joints.
Functions of Skeletal Cartilage: Which Description Of Skeletal Cartilage Is Incorrect
Skeletal cartilage plays a variety of important functions in the body, including:
- Structural support: Skeletal cartilage provides structural support to the body, forming the framework for the rib cage, nose, and other structures.
- Joint function: Skeletal cartilage covers the articular surfaces of joints, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
- Shock absorption: Skeletal cartilage in the intervertebral discs and menisci of the knee helps to absorb shock and protect bones from damage.
- Growth and development: Skeletal cartilage plays a role in the growth and development of bones.
Importance of Skeletal Cartilage
Skeletal cartilage is essential for overall health and well-being. It provides structural support, protects bones, and facilitates movement. Damage or degeneration of skeletal cartilage can lead to a variety of health problems, including osteoarthritis, back pain, and joint injuries.
Maintaining healthy skeletal cartilage is important for preserving mobility, preventing pain, and ensuring overall well-being.
FAQ Insights
What is the primary function of skeletal cartilage?
Providing structural support and protection for bones, joints, and other tissues.
How does skeletal cartilage differ from other types of cartilage?
It is avascular (lacks blood vessels) and contains specialized cells called chondrocytes embedded in a dense matrix.
What are the consequences of skeletal cartilage damage or degeneration?
Reduced mobility, pain, joint instability, and increased susceptibility to osteoarthritis.