Aqueous acetic acid is neutralized by aqueous barium hydroxide – Delving into the intriguing realm of aqueous acetic acid neutralization by aqueous barium hydroxide, this discourse embarks on a journey of chemical reactions and their profound implications. The interplay between these two substances unveils a fascinating dance of protons and hydroxides, culminating in the formation of new compounds and the release of energy.
Prepare to unravel the intricacies of this neutralization reaction, its applications, and its significance in diverse fields.
Aqueous Acetic Acid and Aqueous Barium Hydroxide
Aqueous acetic acid and aqueous barium hydroxide are important chemical compounds with distinct properties and reactivity.
Chemical Properties of Aqueous Acetic Acid
- Weak acid: Partially dissociates in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+).
- Corrosive: Can cause skin irritation and eye damage.
- Sour taste: Gives vinegar its characteristic flavor.
Chemical Properties of Aqueous Barium Hydroxide
- Strong base: Completely dissociates in water, releasing hydroxide ions (OH-).
- Caustic: Can cause severe skin burns and eye damage.
- Bitter taste: Has a distinctive bitter flavor.
Reaction between Aqueous Acetic Acid and Aqueous Barium Hydroxide
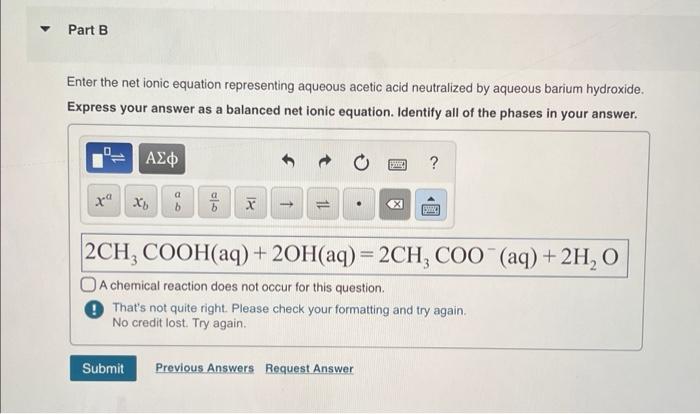
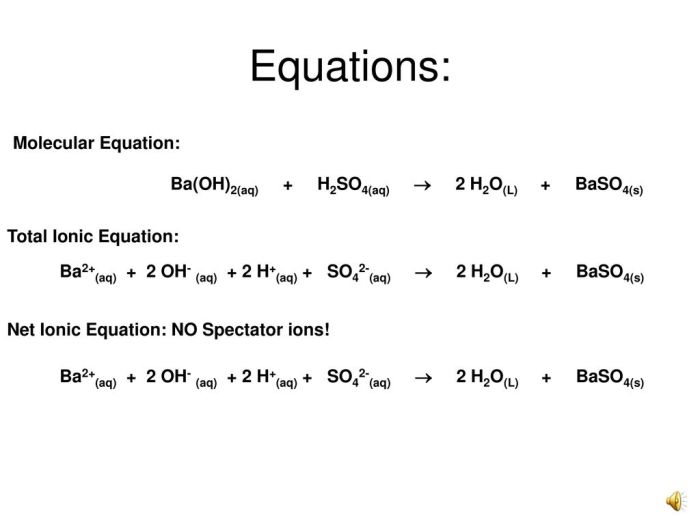
When aqueous acetic acid and aqueous barium hydroxide are mixed, a neutralization reaction occurs. This reaction involves the exchange of protons (H+) from the acid with hydroxide ions (OH-) from the base.
Neutralization Reaction: Aqueous Acetic Acid Is Neutralized By Aqueous Barium Hydroxide
A neutralization reaction is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of salt and water. In this reaction, aqueous acetic acid acts as the acid, while aqueous barium hydroxide acts as the base.
Role of Aqueous Acetic Acid as an Acid, Aqueous acetic acid is neutralized by aqueous barium hydroxide
Aqueous acetic acid donates protons (H+) to the reaction, which are accepted by the hydroxide ions from the base.
Role of Aqueous Barium Hydroxide as a Base
Aqueous barium hydroxide accepts protons (H+) from the acid, resulting in the formation of hydroxide ions (OH-) and water (H2O).
Products of Neutralization
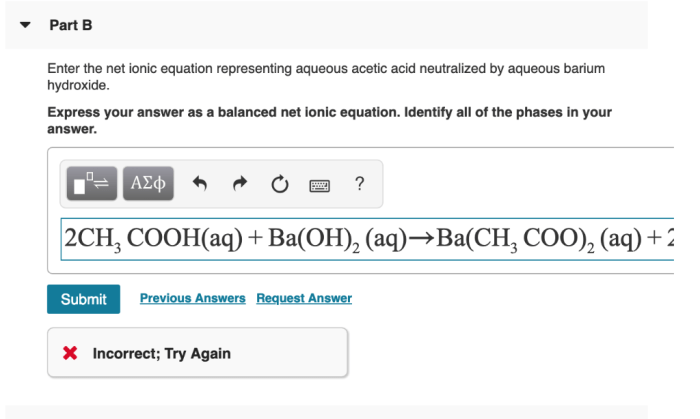
The products of the neutralization reaction between aqueous acetic acid and aqueous barium hydroxide are barium acetate and water.
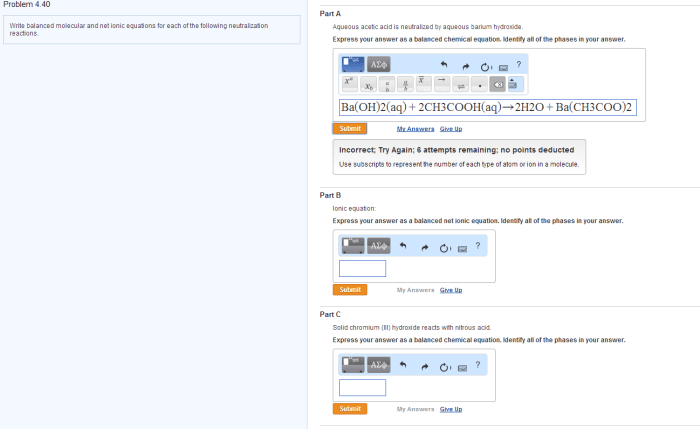
Chemical Equation
CH3COOH (aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) → Ba(CH3COO)2 (aq) + H2O (l)
Significance of the Products
Barium acetate is a salt that is soluble in water. It has various applications, such as in the leather industry and as a mordant in dyeing.
Applications of Neutralization
Neutralization reactions have numerous applications in various fields:
Industrial Applications
- Wastewater treatment: Neutralization of acidic or alkaline wastewater to meet environmental regulations.
- Food industry: Adjusting the pH of food products to enhance flavor and preservation.
- Chemical manufacturing: Producing salts, such as sodium chloride (table salt), through neutralization reactions.
Environmental Implications
- Acid rain mitigation: Neutralization of acidic rainwater by limestone or other alkaline substances.
- Soil pH management: Adjusting soil pH to optimize plant growth and nutrient availability.
- Water purification: Removing acidic or alkaline contaminants from water sources through neutralization.
FAQ Resource
What is the chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between aqueous acetic acid and aqueous barium hydroxide?
CH3COOH(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → Ba(CH3COO)2(aq) + H2O(l)
What are the products of the neutralization reaction?
The products of the neutralization reaction are barium acetate [Ba(CH3COO)2] and water (H2O).
What is the role of aqueous acetic acid in the neutralization reaction?
Aqueous acetic acid acts as the acid in the neutralization reaction, donating protons (H+) to the base.
What is the role of aqueous barium hydroxide in the neutralization reaction?
Aqueous barium hydroxide acts as the base in the neutralization reaction, accepting protons (H+) from the acid.