As “Creating Chains and Webs to Model Ecological Relationships Answers” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with academic rigor and authoritative tone. Prepare to embark on a journey where knowledge is meticulously dissected and presented in an engaging manner, promising an immersive and thought-provoking reading experience.
Ecological relationships form the intricate tapestry of life within ecosystems, shaping their structure, function, and resilience. By unraveling the complexities of these interactions through the lens of chains and webs, we gain invaluable insights into the delicate balance that sustains our planet’s ecosystems.
Ecological Relationships

Ecological relationships are interactions between organisms and their environment, including both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors. These relationships shape the structure and function of ecosystems and influence the distribution, abundance, and behavior of species.
Types of Ecological Relationships
- Predator-Prey:One organism (predator) consumes another (prey) for sustenance.
- Competition:Organisms compete for limited resources, such as food, water, or territory.
- Mutualism:Both organisms benefit from the interaction, such as a plant and a pollinator.
- Commensalism:One organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
- Amensalism:One organism is harmed while the other is unaffected.
Chains and Webs in Modeling Ecological Relationships, Creating chains and webs to model ecological relationships answers
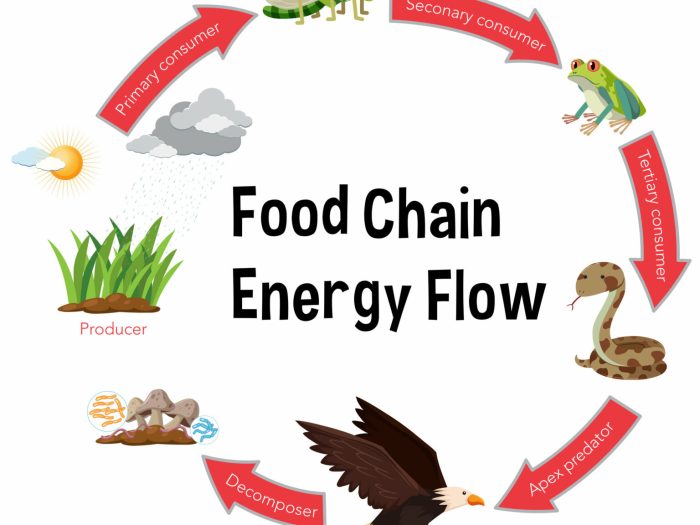
Ecological chains and webs are graphical representations of the flow of energy and nutrients through ecosystems. Chains are linear sequences of organisms, while webs are interconnected networks of multiple chains.
Advantages of Using Chains and Webs
- Visualize complex ecological interactions.
- Identify key species and trophic levels.
- Predict the effects of disturbances on ecosystems.
Limitations of Using Chains and Webs
- Oversimplify complex relationships.
- May not account for indirect interactions.
- Can be difficult to construct for large ecosystems.
Examples of Chains and Webs in Ecosystems
Ecological chains and webs vary across different ecosystems.
Forest Ecosystem
| Trophic Level | Organism |
|---|---|
| Producers | Trees, shrubs |
| Primary Consumers | Herbivores (e.g., deer, rabbits) |
| Secondary Consumers | Carnivores (e.g., wolves, foxes) |
| Tertiary Consumers | Top predators (e.g., eagles, bears) |
Grassland Ecosystem
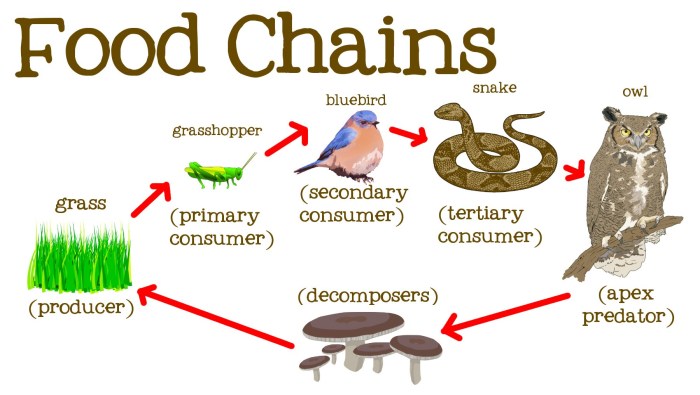
- Grass -> Grasshopper -> Snake -> Hawk
- Grass -> Rabbit -> Fox -> Eagle
Aquatic Ecosystem
- Phytoplankton -> Zooplankton -> Fish -> Seabird
- Seaweed -> Herbivorous Fish -> Carnivorous Fish -> Dolphin
Importance of Chains and Webs in Ecosystem Dynamics
Chains and webs provide insights into ecosystem functioning:
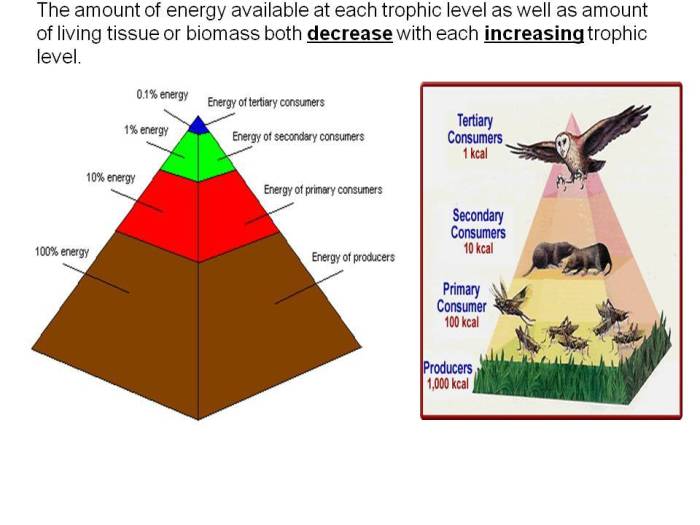
- Energy Flow:Chains show the transfer of energy from producers to consumers.
- Nutrient Cycling:Webs illustrate how nutrients are recycled within ecosystems.
- Stability and Resilience:Chains and webs help maintain ecosystem stability by regulating population sizes and nutrient availability.
Limitations and Challenges in Using Chains and Webs
While useful, chains and webs have limitations:
- Complexity:Ecological relationships are often complex and may not be fully captured by chains and webs.
- Indirect Interactions:Webs may not account for indirect interactions, such as competition or facilitation.
- Temporal Variability:Chains and webs may not reflect seasonal or long-term changes in relationships.
Alternative Approaches
- Network Analysis:Uses mathematical models to analyze complex ecological networks.
- Food Web Dynamics:Examines how food webs change over time and space.
- Ecological Niche Modeling:Predicts the distribution and abundance of species based on their ecological niches.
Answers to Common Questions: Creating Chains And Webs To Model Ecological Relationships Answers
What are the key types of ecological relationships?
Ecological relationships encompass a spectrum of interactions, including predator-prey, competition, mutualism, commensalism, and amensalism, each playing a crucial role in shaping ecosystem dynamics.
How do chains and webs differ in representing ecological relationships?
Chains depict linear sequences of energy transfer, while webs provide a more comprehensive representation of the interconnectedness and complexity of ecological relationships within a community.
What are the advantages of using chains and webs in ecological modeling?
Chains and webs offer a simplified yet powerful framework for visualizing and analyzing the flow of energy and nutrients through ecosystems, aiding in understanding ecosystem structure and function.